The story of 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole tracks with the remarkable changes in organic chemistry since the late 19th century. Early chemists, eager to harness the aromatic structure of benzimidazoles, turned to hydroxy derivatives as they looked for new pharmaceutical agents and dyes. Synthetic routes for benzimidazoles evolved as folks realized those fused ring systems punched above their weight—whether as antifungals or potential anti-tumor compounds. The addition of a hydroxy group at the 2-position stirred excitement, offering a scaffold for hydrogen bonding and electronic effects prized in medicinal chemistry. Over the decades, systematic research in Germany, Japan, and the United States spotlighted this molecule in drug discovery, pigment synthesis, and as an analytical reagent, making it more than just a chemical curiosity.
2-Hydroxybenzimidazole looks unassuming: a beige to pale yellow crystalline powder, stable in a dry bottle, and packed in light-resistant containers to ward off slow decomposition. Its structure offers dual identity—both benzimidazole and phenol—making it a versatile intermediate for chemical industries. With a knack for acting as a chelating agent or a ligand in the coordination chemistry world, it has earned a spot on the laboratory shelf.
This compound comes with a molecular formula of C7H6N2O and a molar mass of 134.14 g/mol. It melts close to 245-250°C, refusing to dissolve in cold water but showing moderate solubility in ethanol and DMSO. The molecule draws attention with its fused aromatic rings and the hydroxyl group that tweaks both its acidity and electron density—factors that affect its reactivity and interactions. The solid resists air oxidation, but sustained exposure to sunlight rarely does it any favors. These features pull double duty in analytical settings and chemical manufacture, where stability under certain conditions matters.
Vendors supply this compound in varying purities, usually marked at 98% and above for research applications. Specifications cover aspects like melting point, water content under 0.5%, and absence of certain heavy metals below international safety thresholds. Labels include batch number, production date, safety pictograms under the Globally Harmonized System (GHS), and recommended storage conditions (well-sealed, cool, and out of direct light). Whether buying a gram for the lab or kilos for pilot plants, tracing and reproducibility ride on careful documentation here.
The common way to make 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole starts with o-phenylenediamine and salicylic acid in a condensation reaction. Researchers discovered that heating these in the presence of acid catalysts, such as polyphosphoric acid or even sulfuric acid, pushes the reaction past the activation barrier, forming the fused rings in a single flask. Some labs opt for microwave-assisted synthesis to speed things up. Yield and purity rise with the right balance between temperature, acid strength, and workup steps. Crystallization from ethanol sharpens up product quality and cuts down on waste. These methods grew out of a need for scalable, cost-effective synthesis, helping the compound find its way into both academia and industrial supply chains.
Chemists often view 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole as a tool for building more elaborate molecules. Its hydroxy group invites etherification or esterification, paving the way for derivatives tailored for photochemistry or drug candidates. The adjacent nitrogen atoms allow for N-alkylation, and in coordination chemistry, the molecule's chelating ability supports metal complexes used as catalysts or sensors. Oxidation or halogenation creates pathways to specialized products, while cross-coupling reactions expand its reach into bioactive analogues. This versatility comes from its aromatic nucleus, which responds well under controlled synthetic conditions.
Folks in different labs or industries may call this compound by many names—2-Hydroxy-1H-benzimidazole, 2-(Hydroxy)benzimidazole, or simply o-Hydroxybenzimidazole. Its registry under the CAS number 529-55-7 ensures clarity in global trade. Specialty suppliers sometimes label it for its role—“benzimidazole-2-ol”—highlighting its hydroxyl function for catalog searches.
Lab work with 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole doesn’t carry exceptional danger, yet it pays to treat it with respect. Inhalation of dust or skin contact calls for gloves, goggles, and an efficient fume hood. Material safety data sheets mark it as harmful if swallowed, irritating to mucous membranes, but it stops short of being acutely toxic or carcinogenic at typical handling doses. Waste must be collected and incinerated according to hazardous organic protocols. These steps fit standard chemical hygiene plans and line up neatly with OSHA and European REACH standards for chemical lab practices.
This molecule pulls weight in pharmaceutical discoveries, crop protection chemicals, and as a stepping stone in dye chemistry. Medicinal chemists lean on its benzimidazole core for designing antiviral, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Agrochemical researchers look for derivatives that hit pests without harming crops. As a corrosion inhibitor, it helps coat metals against harsh environments, thanks to its strong interaction with metal ions. Some labs trust it as a ligand in analysis of trace metals, where its stability and specific reactivity make a difference. Research studies look to its structure when designing fluorescent labels or as building blocks for molecular sensors.
R&D teams across the world turn to 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole for its ability to inspire new chemical reactions and biological studies. In medicinal chemistry, it serves as a core for structure-activity relationship mapping, as researchers swap out side chains and functional groups to tune activity and bioavailability. Materials scientists have begun exploring its potential in organic electronics and as anchoring groups in catalysts. Teams from India to Europe compare it to other benzimidazole derivatives in screening tests for bacterial inhibition, looking to exploit its hydroxy substitution for better target binding or metabolic stability.
Existing data point to low acute toxicity for mammals, but nobody calls it benign just yet. Chronic exposure risks remain under study as regulators and industry groups push for clear data beyond single-dose toxicity. Cell culture studies have flagged moderate cytotoxicity at high concentrations. Regulatory bodies in Europe and North America track workplace exposure levels to protect staff from long-term irritation. Further toxicology profiles examine both metabolic breakdown and potential for environmental persistence, helping scientists decide how to handle and dispose of it without unintended harm.
As research broadens, the relevance of 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole rises in smart material design, advanced pharmaceuticals, and environmental chemistry. Its backbone supports modifications at several positions for tuning electronic, photophysical, or biological behavior. Teams are applying machine learning to suggest new functionalizations and linking patterns that speed up the drug discovery cycle. Early studies in molecular sensors and organic solar cells hint at uncharted applications, especially as the world chases cleaner energy and more effective diagnostics. This compound’s robust core and ease of transformation make it a promising seed crystal for next-generation research.
2-Hydroxybenzimidazole doesn’t sound like a celebrity of the chemical world, but it quietly helps build products most of us touch every day. Chemists and lab workers often reach for this compound as a building block to design molecules for pharmaceuticals, dyes, and even certain types of plastics. These practical uses grow from its structure: the benzimidazole core with a hydroxyl group attached offers versatility that other chemicals can’t match. That little tweak—the addition of the hydroxyl group—makes it more reactive, opening doors for new discoveries.
Drug makers use 2-hydroxybenzimidazole as a starting point for medicines aimed at fighting infections, cancer, and metabolic disorders. Many treatments for ulcers and fungal diseases come from this chemical family. Somewhere in the middle of lab benches and mass spectrometers, researchers reach for this compound to start work on molecules that become active drug ingredients. I remember a research roommate tinkering with benzimidazole derivatives late into the night, searching for compounds that beat tough pathogens. Not all of them made it to market, but without this molecule, those searches stop before they start.
Some of the dyes in our clothes and plastics trace back to 2-hydroxybenzimidazole. Its structure bridges gaps between different chemical groups, which matters because color fastness and durability don’t come easy. Textile manufacturers want dyes that don’t run or fade after a few washes, and this compound helps stabilize the molecular backbone of certain pigment families. More stable dyes means longer-lasting colors for everything from running shoes to industrial wiring jackets. Lab records show companies choosing this building block to fine-tune dye characteristics, looking for a sweet spot between cost, safety, and resistance to sunlight.
Industrial chemists value 2-hydroxybenzimidazole as both a catalyst and an intermediate. In technical terms, it can help speed up key steps without getting consumed—savvy process engineers look for this kind of efficiency. Think of it as the backstage hand that moves props so actors hit their mark. These reactions don’t always grab headlines, but they set the stage for well-known end products, from plastics to polymers. In my own dabbling with chemical reactions, I’ve seen how one tweak—using a compound like this—can cut out wasteful steps. That saves time, raw materials, and energy, and those savings matter when you're running a production plant with tight margins.
Safety data points out that this compound is less hazardous than many alternatives, but it still demands respect. Gloves, goggles, and careful waste disposal never go out of style. Regulatory agencies keep analyzing the impact of common intermediates like these, ready to update rules or suggest handoffs to greener chemicals. Scientists keep searching for less toxic options, but so far, this one balances reactivity with safety better than many rivals.
The story of 2-hydroxybenzimidazole traces the broader arc of innovation: the right building blocks let new discoveries take shape. Whether in medicine, textiles, or industrial chemistry, this compound offers a reliable launchpad for creative problem-solving. I’ve seen firsthand the frustration when a vital reagent runs short. Getting supplies for this versatile chemical means research and manufacturing keep moving—one experiment or factory shift at a time. If chemists ever lose access to flexible molecules like this, whole branches of science could slow down. Watching daily life, it’s easy to miss the unseen scaffolding beneath our medicines and consumer goods. Compounds like 2-hydroxybenzimidazole quietly help hold that scaffolding up.
Spend enough time in a chemistry lab, and you’ll see certain names come up over and over. 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole is one of those. It doesn’t grab headlines, but chemists rely on it for a reason. This compound packs both physical and chemical traits that make it useful beyond textbooks. Recognizing what it brings to the table means appreciating how science touches everyday products, medicine, and research.
Pull out a sample of 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole, and you’ll see a fine, white to off-white crystalline powder. It doesn’t dissolve easily in water, which some folks might see as a hassle. Yet in real-world scenarios, this turns into an advantage—limited solubility means this compound holds up well, even when exposed to humidity. It can take a good amount of heat before breaking down, with a melting point somewhere between 315 and 319 degrees Celsius. I remember struggling once to recrystallize it for a project; it simply refuses to melt or degrade under standard conditions. That tenacity makes it a staple whenever you want a compound that won’t fall apart quickly. You end up reaching for it when other chemicals crumble under heat or moisture.
Looking closer at the structure, you get a benzimidazole skeleton with a hydroxyl group perched at the 2-position. That little difference adds a whole new world of reactivity. With that hydroxyl group, 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole can play both hero and villain in chemical reactions—sometimes acting as an acid, giving up a proton, and other times fitting into hydrogen-bonding roles. These swaps allow it to form bridges between molecules in larger chemical syntheses. In the pharma world, researchers have leaned on it to build drugs with anti-fungal or anti-bacterial properties.
Watching how it reacts with metal ions taught me its coordination skills. It doesn’t just sit there; it forms stable complexes that start popping up in industrial chemistry. I’ve spent hours tracking down odd behavior in test tubes—only to realize 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole was anchoring itself to metal ions, shifting color or solubility right before my eyes. This ability isn’t just a fun quirk; it matters in fields like analytical chemistry, where spotting metal traces can change the outcome of an entire analysis.
If you’ve ever taken a medication that needs to stick around in the body and break down slowly, you might owe thanks to molecules like 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole. Its backbone forms the basis for many drug scaffolds. The challenge comes in handling and formulation. Labs need safer methods for synthesis, limiting exposure to harsh chemicals. Waste from benzimidazole production can bring up environmental questions; a push toward greener chemistry can shrink its footprint.
Universities and companies could work together to develop solvent-free or low-energy synthesis routes. Grants and collaborations go a long way here. Teaching young chemists to recognize the value of compounds like this, both for their reliability and their potential risks, builds a more responsible scientific culture. Technologies for recycling process water, and catching byproducts, already exist—they just need broader adoption for 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole to keep delivering value without extra baggage.
2-Hydroxybenzimidazole shows up in a bunch of labs, especially for folks working with complex chemicals or pharmaceutical research. Its safety doesn’t take a backseat just because it isn't the most explosive or toxic compound around. Skimping on safe storage usually comes back to bite you, whether it’s through accidental ingestion, skin contact, or contamination. From my years dealing with specialty chemicals, I’ve seen what can happen when these details get ignored: burnt fingers, damaged equipment, and ruined research.
I always check the label first. This chemical asks for a cool, dry, and well-ventilated spot. Fluctuating heat, moisture, and sunlight all mess with the stability of organics like this one. A dedicated cabinet away from direct light and humidity protects both people and the substance. Drawers that lock reduce the temptation for accidental “let’s see what happens” moments. Every time a jar sits alongside acids or strong bases, the risk goes up—it’s smart to separate incompatible substances.
Containers should close tightly. Even small gaps let water or air sneak in, causing degradation. Leaving a lid loose once led to a sticky, useless mess I still remember. Getting lazy with seals also raises the chance for contamination. Nobody wants to repeat a full batch because of careless storage.
Simple habits build a safer routine. Gloves and eye protection cut down on the worst risks. It’s easy to underestimate a compound until landing a spill on skin or splashing it near the eyes. One colleague tried skipping gloves “just for a moment” and ended up with irritated, itchy hands for a week. Nitrile gloves do the job, alongside goggles that actually fit—not those loose ones from the bottom of a drawer.
Work at a bench with good ventilation. If a fume hood is available, use it. Breathing in dust or fumes—even at low exposure—never pays off in the long run. I’ve always appreciated bosses who make sure we don't cut corners here. Safety showers and eyewash stations nearby act as critical insurance. Everyone laughs at safety drills until the day someone needs them.
Label everything clearly. Dates, concentrations, and hazards become crucial after a couple of months, especially in a busy lab. Accidentally grabbing the wrong jar in a rush costs time and confidence. Every lid goes back on as soon as possible, no exceptions. If a spill happens, treat it with respect: sweep up solids with care, avoid dust clouds, and wipe surfaces with disposable towels. Wash hands afterward, no matter how quickly cleanup happens. Sharing space with coworkers means one careless spill can cause headaches for everyone.
Training stands out as the best fix for most safety issues. Institutes and companies that put effort into teaching staff do a better job keeping their teams out of harm’s way. I’ve watched teams cut accident rates just by regular refreshers and an open-door policy for “dumb” questions. Personal responsibility, clear protocols, and frequent checkups do far more than any pile of warning labels. In the end, trust in safe storage and handling comes from steady habits built day after day.
2-Hydroxybenzimidazole gets used in labs and factories, mostly as a chemical intermediate for making pharmaceuticals and some plastics. Its powder form flows easily, often turning the air dusty during handling. Breathing in that dust doesn’t just smell unpleasant; it means your lungs end up with a foreign, possibly irritating compound. Getting hands-on with this material calls for a mindset where your health stays number one, not just another line in a standard operating procedure.
Many people I know shrug off gloves and goggles, figuring these steps just slow work down. Skin contact leaves employees with dryness, redness, or cracks from repeated handling—nobody wants that. Masks make breathing less comfortable, but they help keep airway irritation and coughing at bay. Splash goggles shield eyes from even tiny specks that air currents can send flying. Fit-tested respirators—usually an N95 or P100—cut the chance the powder finds its way into your nose or throat.
Labs and industrial work spaces use local exhaust systems over benches and transfer stations, so particles never get a chance to build up. Workers spot leaks by feel or sight, brush material from their sleeves, and vacuum with HEPA filters to avoid stirring up clouds. Wet methods—like damp wipes or mopping—cut dust during cleanup. Open containers on solid, cleanable trays. Never trust a workshop fan to pull up every grain; you need ventilation built for chemicals, not just comfort.
Glass, high-grade plastic, or steel bins with tight lids keep moisture and light away, preserving material stability. Posting hazard signage at every storage point signals caution not just for new staff but for visiting contractors. Temperature swings break down packaging fast, especially if the chemical sits close to a steam line or in a sunny window. If your storeroom smells odd, chances are something’s not sealed as it should be—time for a double check.
Spilled powder on bare skin stings at first, turning into itchy blotches by the end of a shift. Washing right away with soap and water keeps problems small. Eye contact deserves immediate rinsing—fifteen minutes solid under an eyewash station, no skipping out early. Hose down large spills with plenty of water and gather waste with disposable rags. Inhaling fine powder means stepping out to fresh air fast, before symptoms ramp up. Incident logs keep track, so safety improvements can target weak spots instead of leaving them for the next shift to discover.
Newcomers remember basic routines better. Color-coded storage, hands-on demos for donning gloves and masks, and posters describing risks drive those lessons home. Each staff meeting, swapping stories about close calls, helps everyone own the goal of safety. The more often teams spot dangers themselves and speak up, the less likely someone gets hurt or sick.
Trusting personal experience, facts, and a good dose of common sense, real safety with substances like 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole comes down to more than just policy binders. The culture and habits people build shape every day’s outcome in the lab or on the floor.
A lot of folks assume you can just hop online and buy lab chemicals the same way you order batteries or notebooks. Sourcing 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole at the purity levels used in research or manufacturing isn’t that easy. Most average suppliers do not handle this kind of compound. I’ve worked on projects demanding precise chemical purity and learned pretty quickly that you need to know your sources—sometimes you even need to build a rapport with specialty vendors.
Sites like Sigma-Aldrich, Alfa Aesar, and TCI America offer high-purity lab chemicals, including 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole. They hold up to international standards, publish detailed certificates of analysis, and offer batch traceability. Larger chemical companies vet their customers. So, you’ll often fill out account forms or provide proof of academic, industrial, or medical use. A solid supplier never ships something volatile or regulated to a PO box or anonymous customer.
Sometimes folks overlook that impurities in a reagent can scramble results, damage sensitive equipment, or throw off entire research projects. In pharmaceutical or specialized material fields, contaminants can put end users at risk. I’ve seen big projects delayed for months over bad reagents. Make sure the seller can provide a full analysis, not just a rough percentage on their product listing.
There are plenty of chemical sellers online who skirt legal standards, cut corners, or refuse to say where their materials come from. I stay away from sellers without clear communication, a valid business address, or detailed product info. A simple test: ask for the last batch’s analysis or check if the company has a real phone number. Any hesitation is a bad sign. Trusted suppliers make their safety and compliance records open for customers to review.
Rules around chemical sales protect everyone. In the United States and Europe, laws require strict tracking of chemical shipments, background checks for buyers, and reporting for flagged compounds. It can feel like overkill, but the idea is to keep dangerous substances out of the wrong hands. Companies caught ignoring these rules may lose their license, get fined, or worse. Customers sometimes try to dodge regulations with fake info—this never ends well. Respecting these checks builds trust and safeguards your work and reputation.
Every time I needed tough-to-source compounds, I started with local lab supply distributors. Universities and research centers sometimes partner with regional suppliers, which can mean lower shipping costs and easier customer support. Local trade shows or industry seminars become a goldmine for meeting real people instead of anonymous websites. If you don’t see 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole on a supplier’s product page, reach out directly—they might handle special requests or offer advice on safe, legal sourcing.
Order forms for 2-Hydroxybenzimidazole almost always require business credentials. Expect to hand over proof of your role, end-use statements, and sometimes export permits, especially if you’re ordering outside your home country. Keeping your paperwork in order can speed up your first order, prevent confusion, and establish a good reputation with vendors down the line.
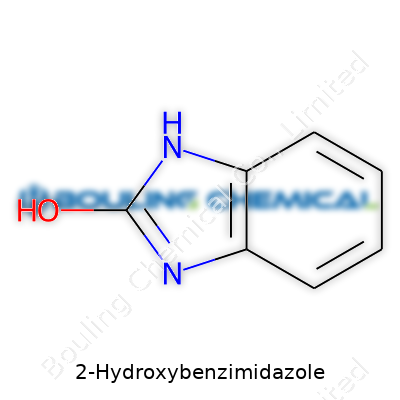
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ol |
| Other names |
2-Oxybenzimidazole 2-Hydroxy-1H-benzimidazole Benzimidazol-2-ol |
| Pronunciation | /tuː-haɪˌdrɒk.siˌbɛnˈzɪmɪd.aː.zɒl/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 615-18-7 |
| Beilstein Reference | 110689 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:38485 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL372078 |
| ChemSpider | 14989 |
| DrugBank | DB08313 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 05b55ac7-09f7-42d2-9002-466202df4f2f |
| EC Number | 2.1.1.1 |
| Gmelin Reference | 7777 |
| KEGG | C14811 |
| MeSH | D000598 |
| PubChem CID | 92267 |
| RTECS number | LU6475000 |
| UNII | 9I4RN2F7EC |
| UN number | Not regulated |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H6N2O |
| Molar mass | 134.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to light yellow powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.36 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | slightly soluble |
| log P | 0.77 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 11.9 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.73 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -57.0×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.751 |
| Dipole moment | 3.92 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 138.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | 133.0 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -2851 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed or inhaled; causes serious eye irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS09 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302: Harmful if swallowed. |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements: "P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 |
| Flash point | > 157°C |
| Autoignition temperature | 705°C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat): > 5000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): >2000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 2~8°C |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Benzimidazole 2-Nitrobenzimidazole 5,6-Dimethyl-2-hydroxybenzimidazole 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 2-Aminobenzimidazole |