Chemists first explored imidazole structures back in the late 1800s. Early researchers, working with what they had on hand, saw that the imidazole ring turned up in plenty of natural compounds crucial to life, like histidine. The push to tweak these rings and create offshoots such as 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole stemmed from curiosity about how small chemical changes affect substance behavior. Over the decades, researchers found more efficient synthetic pathways, making it practical for industrial and research scale use. Manufacturers now build on that foundation with better feeds and purification steps to offer a product fit for tight modern process controls and demanding lab tests.
1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole stands out as a clear, essential intermediate for both fine chemical and pharmaceutical synthesis. Demand comes from its role as a sturdy building block: small enough to invite modifications, robust enough to keep the imidazole character intact. Labs appreciate the versatility. Formulators see real value in customizing this molecule for specialty coatings, ionic liquids, and more, since small shifts in structure can push performance in new directions.
This compound takes shape as a colorless liquid at room temperature. The ethyl group tacked onto the imidazole ring drops its melting point, so it pours freely even in cool labs. Its boiling point runs around 198°C, a mark that matters in both distillation and safety planning. 1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole dissolves smoothly in water, alcohols, and many polar solvents—an asset when fine-tuning reaction conditions. Its pKa hovers around 7, which means it serves well as a mild base and forms solid hydrogen bonds. That's part of the reason it fits nicely in so many chemical and biological environments.
Packages arrive labeled with precise content and purity, often declared at 98% or higher. Trace metals, water content, and known side products appear clear on the certificate of analysis, letting labs gauge risk and suitability for sensitive reactions. Most suppliers provide CAS registry numbers and UN shipping codes plus flammability and toxicity warnings. The material moves in tightly sealed amber bottles or drums to avoid moisture uptake or photodegradation.
Most manufacturers synthesize 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole by alkylating imidazole with ethyl halides such as ethyl bromide or ethyl chloride. This reaction happens under basic conditions, with potassium carbonate or sodium hydride neutralizing the acid byproducts. The controlled addition of reactants, close monitoring of temperature, and stepwise purification guarantee a clean product. Some routes favor phase transfer catalysis for extra efficiency. The finished compound sees distillation under reduced pressure to remove leftover solvents and ensure minimal impurities.
Chemists often reach for 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole as both starting material and catalyst. Its alkyl group opens doors for tailored substitutions at other positions of the imidazole ring. Strong acids or alkyl halides can transform it into quaternary salts—popular as ionic liquids and catalysts. N-alkylation and arylation remain routine in labs tweaking this molecule’s core. The ring’s nitrogen atoms also support metal coordination, which sets up complexes for catalysis, electrochemistry, and sensing. Because of its resilience, 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole tolerates many functional group transformations without losing its backbone.
You may find 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole listed under other names, such as N-ethylimidazole, 1-ethylimidazole, or simply as part of specialty product codes from various suppliers. Its registry numbers bring clarity, but naming can shift depending on regional conventions or manufacturer branding. Major catalogues keep entries cross-referenced to keep customers from mixing up closely related compounds.
Anyone working with 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole needs a clear understanding of its risks. The compound’s low vapor pressure reduces inhalation worries, but splashes or spills still mean gloves and eye protection are a must. Skin contact can cause irritation, especially after repeated exposures. Standard Material Safety Data Sheets note flammability and call for well-ventilated workspaces. Emergency guidance covers spills, fire-fighting, and accidental contact to help with fast action if incidents happen. Storage in tightly sealed containers away from heat and oxidizers helps sidestep unwanted degradation or hazards. Keeping up with evolving workplace safety rules, such as OSHA or REACH, remains part of daily handling.
Science turns to 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole for its versatility. Pharmaceutical labs use it to craft intermediates for anti-fungal, anti-viral, and enzyme inhibitor molecules. This single structure finds its way into ionic liquids—salts that stay liquid at room temperature and boost solvents, batteries, or catalysis. Materials scientists experiment with it as a component in specialty coatings and resins, chasing properties like thermal stability and improved electrical conductivity. Analysts in environmental labs spot-test for derivatives as part of soil and water quality work, since the molecule’s reactivity allows it to appear in various breakdown pathways. Electrochemists value it as a ligand in metal complexes, where the nitrogen atoms tune reactivity and stability.
R&D teams continually tap into the chemistry of 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole, aiming to optimize reactions and expand its applications. Collaborations between industry and academic labs test its performance in next-generation lithium batteries and fuel cells, driven by demands for better charge/discharge cycles. Pharmaceutical companies scour its core structure for new drug scaffolds. Analytical researchers keep mapping degradation products and metabolic pathways, helping meet regulatory guidelines for purity and environmental impact. Green chemistry pushes for milder and solvent-free synthesis methods, while advanced computer modeling speeds up predictions of reactivity and downstream modifications. Every trial and error feeds back into improved protocols and new product launches.
Risk assessment studies show that 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole, while less hazardous than some predecessors, needs careful attention in high doses. Acute exposure can bring irritation to skin, eyes, and respiratory tracts. Chronic, repeated contact risks dermatitis or sensitization, but the overall profile beats many heavier industrial solvents or catalysts. Environmental studies watch for breakdown in water and soil, monitoring both short-lived intermediates and persistence risks. Lab animal models sometimes indicate low bioaccumulation, with rapid metabolization in larger mammals. Regulatory watchdogs still call for clear handling measures and responsible disposal to avoid problems downstream.
Work never stops on improving and reimagining uses for 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole. Chemists seek greener, cleaner synthesis routes using renewable feedstocks and gentler reagents. Industry players hope to scale up production for high-performance materials, such as advanced electrolytes for batteries that outlast today's models. Drug hunters look at the ring structure for new therapies, betting on modifications that boost potency and minimize risks. Increased pressure for sustainability drives adaptation—expect bio-based variants and strategies to reclaim or recycle waste from industrial streams. Digital chemistry and AI-driven design look set to point towards new reactions and materials, promising more value per drop of this adaptable compound.
1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole looks like just another chemical name, but behind that jumble of letters and numbers sits a story that runs through materials labs, pharmaceutical plants, and even electronics manufacturing. I remember the first time I came across this compound during a college internship—midnight in the lab, running small-batch reactions, trying to find the right solvent for a stubborn organic synthesis. 1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole worked where many other chemicals failed.
Drug development teams face hundreds of choices whenever they design new medicines. The structure of imidazole, with its two nitrogen atoms, makes it useful as a base structure in certain drug molecules. 1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole provides slightly different properties than its parent, imidazole. Adding that ethyl group changes how the molecule reacts and interacts with other chemicals, improving solubility or stability. These tweaks can make an inactive compound suddenly become a useful medicine.
Some pharmaceutical chemists use it as a building block to deliver new molecules. In other words, 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole can end up in the final drug or act as a helper, like a catalyst or solvent, during production. Either way, this molecule smooths the road for creative problem-solving in big pharma labs. The FDA expects detailed documentation and evidence, so researchers pay close attention to every step involving it. Transparency and precision remain key.
Modern electronics and corrosion-resistant materials lean on specialty chemicals for their performance. Manufacturers include 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole during the crafting of polymers and resins. It can act as a curing agent for epoxy resins, making finished products tougher and more durable. I’ve talked to engineers who swear by the way imidazole-derivatives fine-tune mechanical and electrical properties. Meeting the demand for faster devices or safer planes ends up in part thanks to the stability and reactivity of these less-glamorous ingredients.
Regulatory oversight here grows stronger every year. Companies have to back up claims with robust testing. Missteps harm not just a business reputation, but human safety. Responsible sourcing and careful waste disposal make a real difference to both workers and the community around a plant.
Chemists and engineers who work with 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole know its benefits and risks up close. Exposure can cause skin or eye irritation. Firms put a lot of effort into protective equipment, training, and ventilation in workspaces to keep people safe. I’ve seen how a single missed glove can mean a trip to the emergency room, so I respect anyone who sticks to the rules every time.
As more industries in Asia and elsewhere boost their production, demand for specialty intermediates like this only climbs. Sustainable practices can’t be an afterthought. Green chemistry offers pathways to safer solvents, recyclable products, and fewer emissions. Regulations can’t keep up unless manufacturers, regulators, and researchers share information and insist on openness and high standards.
The best use of 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole comes with careful documentation, clear communication, and a willingness to innovate for safety. New uses in medicine and manufacturing are likely on the horizon, but guarding health—of both humans and the environment—should guide every project that uses it.
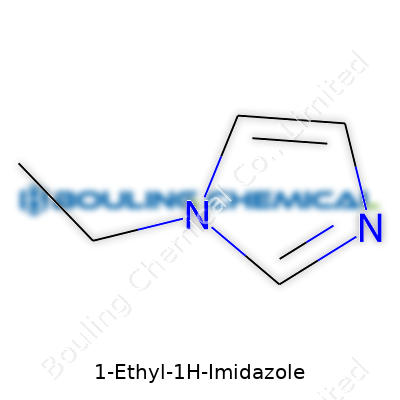
1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole looks a bit mysterious to most people until you pull it apart. Its chemical formula—C5H8N2—won’t turn heads at a dinner party, but it plays an important role in real-world chemistry and biochemical research. Most folks don't consider how adding a simple ethyl group to the classic imidazole ring can nudge its properties just enough to open up new pathways in science and industry.
Starting in a university lab, I remember how easy it was to get lost trying to remember which compound did what. The truth is, formulas act as both a map and a compass. With 1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole, no one gets far without understanding that little tweak to the structure packs a meaningful punch. Add that ethyl group to the standard imidazole ring and you’re not just fiddling with a name—solubility takes a turn, the way the molecule interacts with other chemicals changes, and new applications land on the table.
Lots of drug discovery labs count on small changes like these to create medicines that behave in the body the right way. Toxicologists and safety experts look closely at imidazole derivatives, including 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole, since these can affect how drugs get processed in the liver. The World Health Organization lists imidazoles among antifungal agents, and even a small shift in a formula can spell the difference between a treatment working as intended and a serious health risk.
People sometimes think chemistry only lives in the pages of textbooks. My own projects have proven the opposite—compounds like 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole often end up as building blocks for more complicated pharmaceutical molecules and specialty chemicals. I’ve seen papers tracking how changing that ethyl group alters the molecule’s capability to stabilize metal ions, and even the effectiveness of certain sensors for industrial safety.
Some use 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole as a ligand, helping metals do important work as catalysts. Researchers look at this compound not only for new drugs, but also for high-performance solvents known as ionic liquids. These fluids can dissolve or carry chemicals you just can’t handle any other way. I once watched a chemist swap between imidazole derivatives like ingredients in a recipe, searching for that perfect combination of resilience and low toxicity.
Precision in chemistry goes beyond just memorizing formulas—C5H8N2 draws a line in the sand between safe handling and unnecessary mistakes. Accidents in the lab get less likely with clear formulas, strong labels, and accurate records. Everyone from entry-level technicians to seasoned professors build their protocols around details like these; a misplaced hydrogen atom can mean a very different sort of reactivity, sometimes with harmful results.
Looking at solutions, education comes to mind first. Early, clear exposure to chemical formulas, names, and structural differences builds confidence. On my own journey, strong mentors emphasized not just rote memorization, but making sense of where these compounds fit in the practical world. Industry and academia both benefit from well-illustrated training, clear Material Safety Data Sheets, and regular workshops about relevant chemical families. Meaningful transparency in research also helps: publishing detailed structures and usage data lays the groundwork for the discoveries that follow.
Most people outside of a lab have never heard of 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole. In research and industry, it comes in handy for making pharmaceuticals, specialty plastics, and some agricultural products. If you’ve ever set foot inside a chemistry lab, you’ll know that just because a substance seems bland on paper doesn’t mean you can let your guard down.
This compound releases a sharp odor, which hits you fast if a bottle opens in a small room. It’s not as infamous as some other chemicals for hazardous health effects, yet the structure gives it some bite. The imidazole ring can irritate skin and the respiratory tract. Spills on bare skin sting, and breathing in vapors leads to a burning in the nose or throat. The same applies to other imidazoles: their basic nature tends to disrupt the body’s chemistry at the contact point.
Safety data sheets, or SDSs, show plenty of warnings: wear gloves, goggles, and keep a fume hood open. Eye contact means trouble—redness and even temporary vision changes, based on cases people shared online. Once, during a grad school project, a classmate tried to pipette it by mouth as a joke. The results weren’t funny at all: headache, sore throat, and a reprimand from the safety officer. Even diluted, the stuff demanded respect.
Handling it isn’t a game of chance. Gloves become non-negotiable: the lightweight latex or nitrile ones work. No one sane tries to work with this in an unventilated room. Open containers under a fume hood, and keep spill kits nearby. A small drip on the bench can turn into an unpleasant experience if wiped with a bare hand. Wearing a lab coat with sleeves covers arms, and face shields give peace of mind for splashy jobs.
I learned early from a mentor that carelessness comes back to haunt you. A single poor decision, like pouring used solvent down the wrong drain or tossing a saturated rag, sets up a giant headache later on if someone gets exposed. Keeping safety routines strict not only prevents skin rashes or headaches, it also keeps work disruptions out of your day. In busy labs, workers encourage a habit of running through checklists before opening any hazardous liquid. Most people I know prefer erring on the side of overprotection after seeing what even relatively mild imidazoles can do.
Many workplaces try to cut corners by skipping fume hoods or buying lower-grade gloves. Management often figures minor irritation isn’t a big deal. Yet the truth is, even mild chemicals create uncomfortable—and sometimes expensive—incidents if treated carelessly. Stress, inattention, and tiredness bury good habits. Regular, focused training brings attention back where it belongs.
For anyone designing policies, it helps to base exposure limits on real incident data and not just chemical books. Labs that invite open discussion about near-misses and close calls give workers a chance to learn. The best thing about science workplaces is their ability to adapt fast when someone speaks up.
1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole does not rank as a supervillain in the chemical world, but it definitely carries a few rough edges. Clear routines, good protective gear, and an attitude that respects the power of chemicals make a huge difference. Watching out for sharp-smelling bottles in the storeroom never hurts, either.
Anyone working in a lab or around fine chemicals knows the importance of storage. 1-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole sits on a long list of reagents that demand respect. Maybe it's tempting to think one small bottle won't matter, but poor storage decisions quickly lead to leaky caps and evaporating product. Besides the money wasted, careless handling can put personal health and air quality at risk. When a chemical gives off fumes or reacts with water, you remember those safety lessons for years.
It rarely pays to ignore the recommendations from manufacturers. Almost every supply sheet points straight to storing 1-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated place. Heat encourages volatility. Some labs, short on space, put sensitive reagents just anywhere. In that bustle, solvents and reagents end up near radiators or sunlit windows, only to show discoloration or thickening weeks later. Once, a coworker stored a similar imidazole in a warm spot. The smell soon warned everyone that things weren’t right. The lesson stuck: chemicals want peace and shade.
Moisture eats away at the purity of both imidazoles and the glassware that holds them. Humid air sneaks into uncapped jars during busy prep work, so proper sealing can't be skipped. Sealing containers tightly not only keeps out the air but stops spills during routine shelf checks. Those who work in shared spaces have seen what a loose cap does. Odors spread fast, and sometimes a white crust appears at the bottle’s rim, a clear mark that water and air got inside. Working with gloves and checking caps after each use sounds simple, yet schedules often turn these steps into afterthoughts.
Any changes to the color or odor of 1-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole deserve attention. Clean, uncontaminated reagent should never have a strange tint or particulates. I once ignored a slight shift in color, thinking it was just dust. Later analysis proved the chemical degraded. That waste of time and product could have been avoided by catching the early warning signs. No matter the daily pressures, keeping an eye on these signals saves both effort and money down the line.
Each lab setup comes with limitations, but some simple habits protect reagents. Store 1-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole away from acids, bases, and oxidizers if possible. Segregation by compatibility can’t be overstated. Cabinets designed for chemical storage with good ventilation stop fumes from filling up small rooms. Never stack bottles so high they risk falling in the rush of a busy day. For lighter-sensitive products, an amber glass bottle helps block out stray light. Even in a pinch for time, labeling your bottle with both the opening date and last check avoids confusion later.
Most storage missteps stem from haste or trying to save on storage costs. Investing in better shelving, proper vented cabinets, and consistent labeling saves on ruined chemicals and lost lab time. Chemical safety data sheets, though often glanced over, offer a goldmine of advice—worth reading before the first pour. For those new to handling 1-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole, take a few minutes to check the supplier's recommendations. For seasoned hands, modeling these habits helps set the right tone for new lab members. Peace of mind and worker safety remain the real rewards for careful chemical storage.
Every bottle or drum labeled as 1-Ethyl-1H-imidazole represents more than just a name on a sticker. Scientists, lab managers, and quality control techs all look beyond the label and zero in on purity. Getting the right answer unlocks confidence in experiments, manufacturing, or scale-up. In my own days helping a polymer lab sort batches for pilot production, purity was the dealbreaker. No one enjoys chasing down a failed reaction only to discover impurities as the culprit.
So, what exactly is “purity” here? Most chemists define it as the percentage of the main compound in the sample, free from by-products, solvents, or unreacted starting chemicals. Reliable suppliers usually offer purity ranges between 97% and 99%, sometimes higher, depending on the synthesis and purification method. Checking a certificate of analysis tells most of the story—look for GC, HPLC, or NMR numbers, not just a ballpark guess.
A compound’s job changes with the setting. Researchers doing organic synthesis need clean imidazoles to keep side reactions under control. In pharmaceuticals or agrochemicals, even trace leftovers can skew results or risk safety. The raw material’s purity influences shelf life, color, and even the promise you can make to regulators.
From the trenches: a former colleague once shared their struggles with a polymerization project that stalled repeatedly. Turns out, the 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole on hand barely scraped past 95% purity, and each run saw unpredictable shifts in end-use properties. Only once they got a confirmed 99% supply did the wildcards stop.
Trust in a product starts with transparency. Companies should disclose details behind their purity claims—batch numbers, certificates of analysis, and information about the test methods. If a supplier is evasive or slow to deliver data, that sends up red flags. I’ve seen teams lose weeks waiting for documents that should have come with the first shipment.
There’s more at stake here than lab headaches. End-users must keep their operations safe and reliable. According to a recent report from Chemical & Engineering News, even pharmaceutical recalls have traced their roots to impurities overlooked in critical feedstocks. Choosing suppliers who invest in thorough in-house testing—and who share raw chromatograms or spectra, not just summaries—offers real security.
Customers can hold suppliers to higher standards. Ask for sample COAs before that first order. Where the stakes are high, consider running an in-house confirmation (many labs keep GC or NMR routines for such vetting). Skipping background checks might look efficient in the moment, but few shortcuts end well in science.
If supply gaps force you into a lower-purity batch, map out the risks. Do performance-critical steps tolerate an extra fraction of an impurity? Some applications can accept less stringent specs, but those decisions demand testing, documentation, and clear communication throughout the supply chain.
Every research or production line counts on what goes in as much as what comes out. Checking and confirming the purity of 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole lays the groundwork for success long after the first bottle is opened. From benchtop to big batch, purity is not a luxury—it’s the baseline.

| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 1-ethyl-1H-imidazole |
| Other names |
1-Ethylimidazole N-Ethylimidazole |
| Pronunciation | /ˈwʌn ˈiːθəl wʌn eɪtʃ ɪˈmɪdəˌzoʊl/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 120-68-3 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | `3D Structure;JSmol;C1=CN(C=N1)CC` |
| Beilstein Reference | 505984 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:83546 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL60793 |
| ChemSpider | 68419 |
| DrugBank | DB02142 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03b19ce6-7760-48c9-af7b-c5e797911a7c |
| EC Number | 219-237-7 |
| Gmelin Reference | 78620 |
| KEGG | C06317 |
| MeSH | D020011 |
| PubChem CID | 6970 |
| RTECS number | NL1575000 |
| UNII | B3F7Y2B0YB |
| UN number | UN1992 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H8N2 |
| Molar mass | 110.15 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | amine-like |
| Density | 0.997 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| log P | 0.02 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.463 mmHg at 25 °C |
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.1 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 7.13 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -41.6·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.490 |
| Viscosity | 2.53 mPa·s (25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 2.83 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 173.7 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | 32.3 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -3385 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H302, H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P280, P261, P305+P351+P338, P304+P340, P312 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-2-0 |
| Flash point | 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) |
| Autoignition temperature | 355°C |
| Explosive limits | 1.5-11.4% (V) |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD₅₀ (oral, rat): 1300 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): 1300 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | WA1730000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 0.5 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Imidazole 1-Methylimidazole 2-Ethylimidazole 4-Ethylimidazole 1,2-Dimethylimidazole 1-Propylimidazole Benzimidazole Histidine |