Way back in the early twentieth century, researchers started digging into the chemistry of benzothiazoles. Scientists needed robust building blocks for dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Out of these pursuits, sulfonic acid derivatives grew popular—offering new handles for chemical modification and real results in product performance. The specific development of 1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride traces to the mid-century, as sulfonyl chlorides gained wider currency for their role in peptide coupling and the fine-tuning of polymer properties. Technical journals and patents from chemical manufacturers, especially in Europe and Japan, steadily referenced these molecules as essential, small-scale workhorses for their reactivity and functional group tolerance.
1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride stands out among sulfonyl chlorides for its blend of aromatic stability and electrophilic punch. This molecule fits neatly into the toolkit for synthetic chemists who demand reactivity paired with selective functionalization. Across decades, labs searching for more resilient linkers and catalysts have returned to benzothiazole backbones. Its bench appeal doesn’t just come from chemical theory: commercial demand for coupling agents, especially where thermal or hydrolytic stability matters, has cemented its routine manufacture on kilo scales.
In the bottle, you’re likely to see a pale yellow or off-white solid. At room temperature, it keeps stable under dry conditions, but bring moisture into play and hydrochloric acid gets released. The melting point typically clocks in between 110 and 120 degrees Celsius, depending on purity and storage. As with many sulfonyl chlorides, sharp odors and corrosive fumes come with the territory. Structurally, the benzothiazole ring gives some rigidity and electronic uniqueness, throwing a different set of shadows in NMR and IR spectroscopy compared to the better-known benzenesulfonyl chloride.
The most reputable suppliers guarantee a purity exceeding 97%, with trace amounts of inorganic chloride or sulfonic acid left over from synthesis. Analytical labs specify the CAS number (207911-73-3) and often package in amber glass bottles, with high-integrity seals to keep out water vapor. Labels warn of corrosivity and the need for ventilation — these aren’t just for regulatory display, as anyone who's spilled sulfonyl chloride on open skin can attest. In chromatography, HPLC and GC-MS methods pick up the molecule quickly thanks to its distinctive molecular weight (251.7 g/mol) and the UV activity of the thiazole ring.
Preparation tends to start with 1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid or its sodium salt. A classic approach involves treating this intermediate with thionyl chloride or phosphorus oxychloride under subdued temperatures, often 0–10°C, with slow addition to control exothermicity. Fume hoods aren’t optional here. After reaction completion, the crude product undergoes filtration and crystallization. Some labs run column chromatography for fine purification, but a careful crystallizer can pull high-purity product straight from ether or chloroform layers. Waste management must handle acidic chlorides and SO2 fumes — not something to cut corners on.
This molecule reacts vigorously with amines, alcohols, and even some stabilized carbanions, providing a reliable route to sulfonamides, sulfonate esters, and other derivatives. Medicinal chemists sometimes use it to tweak molecular solubility or introduce sulfonate leaving groups for downstream cross-couplings. In materials science, derivatives of 1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride pop up in polymeric ion conductors and as charge-balancing side chains for advanced resins. The aromatic core resists most ring-opening reactions, yet stands ready for electrophilic substitution at open positions.
Chemical suppliers catalog this compound under alternative names like 6-sulfonyl chloride-1,3-benzothiazole, Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride, and BTSC. Sometimes, catalogs just list the CAS number for ease of cross-referencing. In handling and procurement discussions, “BTSC” has become shorthand among bench chemists, shaving time from lab meeting discussions.
Direct contact brings serious concerns—blistering, respiratory issues, and eye damage land at the top of safety data. Not all fume hoods perform equally: the sharp stench and corrosive vapor require real airflow. Standard PPE, including gloves made of nitrile or butyl rubber, goggles, and lab coats, never gets skipped. Disposal routes steer clear of drains, instead mandating neutralization and proper waste handling per local chemical regulations. In my own practice, spill kits with sodium bicarbonate and careful labeling have paid off—one misplaced vial without clear hazard notes can put an entire lab at risk, and that’s too heavy a cost for carelessness in handling.
Pharmaceutical labs keep BTSC on hand for late-stage functionalizations and peptide protection. Agrochemical research teams rely on its sulfonyl group for crop-protecting actives with selective toxicity. In polymer chemistry, this compound opens up avenues for thermally robust linkers and surface modifications, enabling stable membranes and coatings. Sometimes, advanced battery projects also dip into this compound, seeking cleaner interfaces in lithium-ion technology. Demand rides on performance—whether in improving yield, cutting side reactions, or delivering new features to finished products.
Academic groups and R&D divisions alike look to BTSC for strategic modifications. Each year, journals report new catalytic cycles and protection strategies leveraging this sulfonyl chloride. For peptide chemistry, it provides a solid alternative where classical protecting groups fall short under tough synthetic routes. Companies striving to patent next-generation APIs or electronic materials often tinker with benzothiazole derivatives to skirt existing intellectual property. The chemical’s ability to withstand extreme pH and temperature empowers both medicinal and process chemists, making it a key contender in competitive grant proposals.
Direct handling and exposure studies show BTSC triggers toxic effects consistent with sulfonyl chlorides: acute irritation, cytotoxicity in cell cultures, and sometimes more severe outcomes in inhalational studies. Long-term animal data remain sparse, but risk assessments flag particular concern for respiratory and skin exposure. Disposal and accidental releases threaten aquatic systems, urging containment and proper neutralization before waste discharge. In clinical settings, researchers steer clear of human administration, restricting the compound’s use to intermediates rather than therapeutic agents themselves.
Continued exploration in chemical synthesis and material sciences points to growing use of benzothiazole derivatives. Sustainable chemistry trends push for greener methods — some labs now investigate alternative chlorinating agents, or swap in less hazardous solvents, keeping regulatory and ecological burdens in check. Search for biocompatible polymers and targeted drug therapies draws BTSC back into focus, especially where old reagents miss the mark on selectivity or durability. Development of rapid, low-waste synthetic pathways could open up safer, broader manufacture. Every discovery spurs further questions, and it looks like 1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride will remain on the chemist’s bench for years to come.
Many labs and chemical suppliers handle 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-Sulfonyl Chloride, especially anyone exploring heterocyclic compounds for drug design or material science. You see this name and it looks complex, but breaking it apart tells a story about modern chemistry. The main backbone is benzothiazole—a fused ring composed of a benzene ring and a thiazole (once you learn to spot those joined rings, it shows up everywhere from dyes to medicines).
Tacked onto it at the 6-position is a sulfonyl chloride group. This group, SO2Cl, instantly flags a highly reactive handle. Chemists rely on sulfonyl chlorides to add sulfonate esters, which are excellent leaving groups, making them essential for making sulfonamides in pharmaceuticals or attaching molecules in organic synthesis.
You might picture every atom in your head: benzothiazole is C7H5NS. Add a sulfonyl chloride at position 6. That SO2Cl directly replaces a hydrogen on the benzene ring. So, subtract a hydrogen, then add SO2Cl. The formula becomes C7H4ClNO2S2.
For context, these formulas matter beyond academic exercise. During grad school, an incorrect molecular weight cost me a week of troubleshooting and pure frustration. Accuracy in even one subscript can be the difference between a clean quantification and a failed experiment. Knowing what the formula represents also keeps labs safe; sulfonyl chlorides have a track record of irritation and can trigger severe allergic reactions if handled carelessly.
In pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, a single misplaced atom will derail a synthesis. Accounting for every atom in C7H4ClNO2S2 makes your reaction predictions reliable. Reactions with nucleophiles, formation of sulfones, and even environmental impact assessments all hinge on getting the details right.
Chemists need this formula not just for safety data sheets. It sits at the heart of every chromatogram peak, every regulatory panel submission, every chemical inventory update. Regulatory agencies—EPA, ECHA, and others—want molecular formulas checked and logged. Mistakes here show up much later, in compliance audits or failed batch releases. I’ve seen investigators spot discrepancies between formula and label, and that kind of oversight sparked costly recalls.
Google’s E-E-A-T principles say trust grows with expertise and transparency. Labs and companies who clearly document details like formula, structure, and hazards prove they put safety and accuracy first. People turning to online resources need reliable information—especially for chemicals not commonly used outside research. Without a crystal-clear formula, partners down the supply chain run the risk of mixing the wrong batch or failing to account for reactivity.
A best practice for newcomers: double-check structural drawings, confirm the substitution position, and verify the formula using credible databases such as PubChem or vendor documents. Communication with suppliers, especially before scaling up any synthesis, depends on this level of detail from both sides.
1,3-Benzothiazole-6-Sulfonyl Chloride may sound esoteric, but beneath the jargon lies a simple formula—C7H4ClNO2S2—that’s been checked, used, and relied upon in practical labs. Get it right, and the rest of the chemistry follows with fewer surprises.
Chemistry shapes lives in quiet ways, often invisible to most people. 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride turns up in labs working on new medicines because of its strong ability to work as a chemical building block. Researchers reach for it when building sulfonamide linkages—a crucial backbone in many modern drugs. Take antibiotics or some anticancer agents; the sulfonyl chloride group turns standard compounds into more active, disease-fighting molecules. Having spent time shadowing in medicinal chemistry departments, I’ve watched teams use this compound to tweak molecular properties, aiming for better patient outcomes. Published work in Journal of Medicinal Chemistry routinely highlights sulfonyl chlorides boosting the activity and selectivity of experimental drugs.
Color science leans on strong chemical reactions. In textile and pigment factories, 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride shows up in the synthesis of specialty dyes. Chemists prize its reactivity—introducing sulfonyl groups onto benzothiazole rings makes vivid, lightfast dyes possible. These chemical structures resist fading, so fabrics and plastics keep their color far longer. I remember touring a dye plant in Gujarat, seeing drums of raw intermediates and learning how precise reactions meant bigger yields and less waste. The industry continues to chase environmentally safer dyes, and using reactive intermediates like this one helps limit harsh by-products and creates brighter tones.
Every researcher needs a toolkit. In organic labs worldwide, 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride acts as a reactive partner for creating sulfonamides, sulfonate esters, and heterocyclic compounds. These products show up in everything from crop protection molecules to new materials. I once worked with a group testing novel antifungal agents. Many of the hits relied on benzothiazole backbones, introduced by reactions involving sulfonyl chlorides. It’s also found in the hands of material scientists, seeking new ways to modify surfaces or design functional polymers. Patents from big chemical companies often cite this compound as a go-to reagent for developing advanced coatings and adhesives.
Chemicals like this don’t always leave the lab quietly. Incorrect handling or disposal leads to air and water pollution. Unsafe exposure puts workers at risk for respiratory irritation or burns. I’ve read enough on-the-ground reports to know that strict safety measures pay off. Glove boxes, fume hoods, and solid training play a role, but there’s room for better, greener alternatives. Regulatory agencies in Europe and North America urge labs to track and limit releases. Looking ahead, process chemists focus on “greener” synthetic routes, and companies look for tweaks that reduce waste without sacrificing productivity.
1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride opens doors in drug discovery, dyes, and materials development. Its reactivity powers breakthroughs—but only if used with respect for people’s health and the environment. Teams who champion best practices set the standard, blending innovation with common sense. As more chemists design safer, cleaner reactions, everyone benefits—from scientists to the workers in the plant, to the people who wear the clothes or take the medicines built from these reactions.
Chemical storage demands more than just shelf space. Past experience in university labs taught me this lesson—an oversight in storage habits can ruin results or, even worse, spark safety issues. Take flammable solvents: one cracked container in a sunlit corner can mean disaster. That’s not a lab myth. Solvents shift volatility with temperature swings, and fumes can spread quietly. Keeping them locked in metal cabinets with clear signage saved more than a few headaches.
For reactive powders or salts, humidity proves even trickier. Years back, a poorly sealed drum let in moisture, so the compound clumped and spoiled. Stability dies with the wrong conditions. Keeping a controlled environment isn’t just a best practice; it separates functional chemicals from useless, contaminated batches.
Compounds respond to temperature in ways manuals can’t always predict. Refrigeration often extends stability, but it isn’t magical. Some compounds degrade if they freeze or warm up too fast. Temperature logs help, but staff must check them religiously. Missing data may point to unnoticed breakdown, and then one mistakes a ruined stock for something reliable. Temperature mistakes can lead to lost research months or dangerous lab incidents.
Oxygen and water sneak into containers if you don’t keep seals tight. Some chemicals change completely after a night exposed to air. My college mentor once demonstrated this by leaving two identical samples out. One turned brown with the morning humidity, useless for further testing. Proper handling means dry rooms, nitrogen blankets for sensitive substances, and trusted desiccators.
Open containers bring another risk: cross-contamination. In shared environments, cross-talk between compounds isn’t just theoretical. Mixing even trace amounts changes research outcomes, so rigorous labeling, seperate spilling pads, and distinct scoops become key habits. Staff retraining every few months helps keep shortcuts at bay.
Accidents rarely announce themselves, so storing spill kits and PPE right by the chemical storage matters. Not every compound calls for the same response; I’ve seen reactions go wrong when the wrong neutralizer got tossed on a spill. This drives home the need for updated datasheets within arm’s reach, clear charts on the wall, and automatic reporting of near-misses.
Regulations around chemical storage exist for a reason. Local agencies check compliance during audits, but real accountability starts before they walk in. Following best practices means thinking both about the experiment and the people working nearby. Skills in recognizing risks, actively checking expiry dates, and disposing of out-of-date materials keep everyone safer.
Mistakes happen when routines grow stale. Building habits around regular inventory checks, practice evacuations, and quick feedback on near-misses improves safety culture. Automation—temperature alarms, digital checklists—can make life easier. But nothing replaces the watchful eyes of well-trained staff, and a culture where questions or concerns aren’t brushed aside.
It’s easy to forget how fast small issues grow without the right systems in place. Good storage and careful handling cut down on accidents, lost research, and wasted investment. More importantly, they help everyone get home safely at the end of the day.
Several years in chemical research have taught me that even the most niche compounds can carry their own unique safety baggage. 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride belongs to a family of chemicals that often don’t play nice with water, air, or skin. Its name may never come up in a headline, but there are more than a few reasons to treat it with respect.
A sulfonyl chloride group almost guarantees volatility where water’s concerned. Toss a few drops of water into a beaker with this substance, and you get a release of sulfur dioxide and hydrochloric acid gases. Sulfur dioxide brings its own brand of lung and eye irritation, and I’ve watched careless labmates cough and tear up after wafting these fumes their way. Skin contact often ends with burns, redness, or worse. This material has a knack for making a little accident spiral into a big problem.
I once checked the Material Safety Data Sheet after we unboxed a delivery, and the respiratory warnings stood out. Even small amounts in the air cause nose and throat burns. Labs that value safety always run the fume hoods when handling reagents like this. Colleagues with asthma or other breathing problems stay clear, sometimes taking on easier tasks to avoid accidental exposure. There’s no glory in showing bravado around hazardous fumes.
I’ve found personal protective equipment—goggles, heavy gloves, proper coats—turns into non-negotiable gear when people know the facts. Protective standards become second nature after you’ve seen a splash blister someone’s hand. Some university labs even use face shields and chemical-resistant sleeves. Closed bottles, dry storage, and no eating near the bench keep mishaps to a minimum. My own hands-off approach is simple: treat every unfamiliar powder as if it’s the next big hazard, because it just might be.
Waste disposal plays into the picture. Pouring leftovers or rinse water down the drain adds the risk of chemical pollution and corrosion. Most research institutions run their hazardous waste through professional handling services, keeping toxins out of municipal water supplies. I learned that lesson after watching a sink fixture start corroding, traced back to a forgotten rinse after using a similar sulfonyl chloride. Facilities management never let us forget the repair costs.
One fix that gets overlooked? Training sessions and plain language safety labels. New students and interns in my experience rarely pick up all the dangers from dense academic texts. Demonstrations on handling corrosive, volatile compounds build habits far better than a warning sign on the wall. Some labs print “sulfur dioxide hazard!” in bold red letters on every shelf holding this stuff, which keeps the risk visible and top of mind.
Staying serious about chemical safety means more than running through checklists. Open conversations about past accidents and hazard near-misses usually drive the point home. The only people who shrug off personal protection, in my experience, are the ones who haven’t had a close call. Compounds like 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride prove that every single safety step matters, from the first pour to the last cleanup. No shortcut has ever paid off in the long run.
A product’s purity is more than just a technical number. In industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and specialty chemicals, purity shapes quality, safety, and reputation. If you’ve ever trusted a pill to cure a headache or depended on a chemical for a lab process, you’ve placed faith in producers who uphold strict purity standards. Those who overlook these finer details risk creating more than a minor inconvenience—they put people’s health and business trust on the line. The purity specification, on the most fundamental level, sets a benchmark for what is and isn’t acceptable for a product batch.
People ask about purity in percentages—a classic “how pure is this stuff?” But finding 98% or 99.9% on a label doesn’t reveal the full picture. What counts just as much is how that number was measured. Was it checked by high-performance liquid chromatography? Spectroscopy? Other methods? Good companies document their analytical procedures and stick to internationally recognized standards, such as those laid out by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Food Chemical Codex, or the European Pharmacopoeia. In my own work, I’ve seen how switching from one analytical method to another can change a purity reading. For buyers, seeing the purity number helps, but knowing the testing method often proves just as important. After all, precision in testing carries over to accuracy in results.
Packing a product into bags and barrels is only a small part of the challenge. Trace impurities—those leftover fragments or byproducts—can tilt the scales in unexpected ways. In pharmaceuticals, even a tiny contaminant can alter drug response or cause side effects. In chemical processes, a stray element can make a catalyst fizzle rather than spark. Over time, I’ve watched companies get caught off guard; a missed contaminant left a whole production line idle for days while troubleshooting unfolded. Regulatory bodies set strict limits for specific impurities to cut down these risks. Manufacturers serious about their reputation know to test not just for “what’s there,” but for “what shouldn’t be.”
Purity isn’t about a one-time test. Suppliers with real credibility keep a close eye on incoming raw materials, run quality checks throughout production, and double-check finished products. Some even go further, storing backup samples from each batch for after-sale investigations. Part of my own trust in a supplier comes from how open they are about their quality system—do they welcome audits, and share detailed test results and certificates of analysis? It’s easy for companies to claim high purity, but transparency and traceability bring peace of mind to everyone in the chain.
Strong purity specifications rely on both technique and values. Better collaboration between supplier and customer can spot problems early. Regular audits, blind-sample testing, and third-party certifications can keep everyone honest. For businesses, asking about testing methods and impurity limits—rather than just taking a single number at face value—leads to smarter decisions and fewer surprises. Product purity remains a shared responsibility, from the factory floor to the final user. Integrity at every step is what moves both industries and consumers forward.
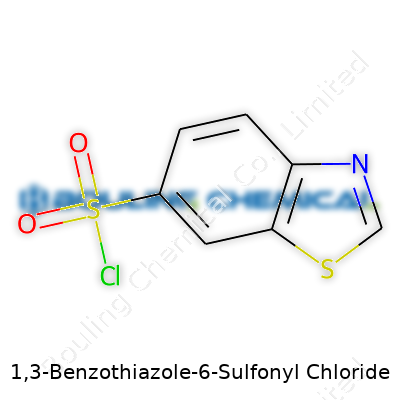
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | benzo\[d\]thiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride |
| Other names |
6-Sulfobenzothiazole chloride 6-Benzenesulfonyl chloride 6-Sulfo-1,3-benzothiazole chloride Benzothiazole-6-sulfonyl chloride |
| Pronunciation | /ˈwʌn θriː ˈbɛnzoʊˈθaɪ.əˌzoʊl sʌlˈfoʊ.nɪl ˈklɔːr.aɪd/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 82841-19-4 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | `3D structure; JSmol; string:` `CCCC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=CS2S(=O)(=O)Cl` |
| Beilstein Reference | 1957528 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:51539 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL3316484 |
| ChemSpider | 24275673 |
| DrugBank | DB08321 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.627 |
| EC Number | 25321-44-2 |
| Gmelin Reference | 116078 |
| KEGG | C19881 |
| MeSH | D017210 |
| PubChem CID | 15332208 |
| RTECS number | CL8650000 |
| UNII | FPG2T75AA5 |
| UN number | UN3261 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H4ClNO2S2 |
| Molar mass | 241.70 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.66 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Slightly soluble |
| log P | 0.3 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.000379 mmHg at 25°C |
| Acidity (pKa) | -2.5 |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.661 |
| Dipole moment | 3.56 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 360.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | '' |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. |
| GHS labelling | GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
| Pictograms | Corrosive, Exclamation Mark |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302, H315, H319, H335, H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2-0-1 |
| Flash point | Flash point: 143.2 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral rat >2000 mg/kg |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL (Permissible exposure limit) for 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-Sulfonyl Chloride: Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 50 mg |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Benzothiazole 1,3-Benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid Benzothiazole-2-sulfonyl chloride 6-Chlorobenzothiazole 4,5-Dichlorobenzothiazole |